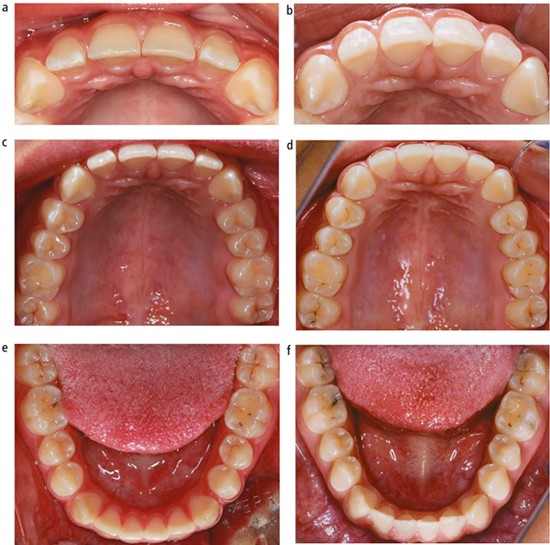
Tooth erosion, also known as dental erosion or acid erosion, is the gradual loss of tooth enamel caused by the exposure to acidic substances. Tooth enamel is the hard, protective outer layer of your teeth, and when it wears away, it can lead to tooth sensitivity, discoloration, and increased susceptibility to cavities. There are several causes of tooth erosion, and it's important to understand them in order to prevent and treat it effectively.
Treatment for tooth erosion depends on the extent of enamel damage:
It's essential to consult with a dentist if you suspect tooth erosion or experience symptoms like increased sensitivity, discoloration, or tooth pain. Early intervention can help prevent further damage and maintain your oral health