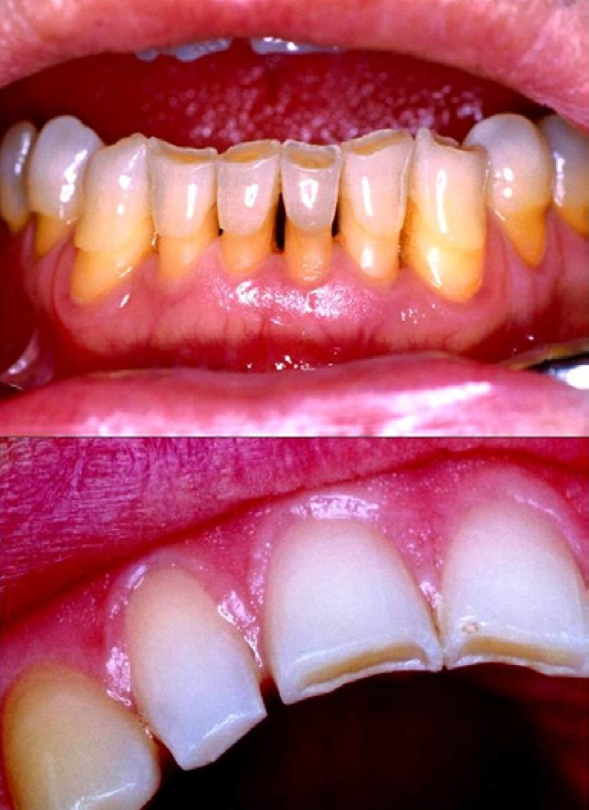
Teeth attrition is the process of gradual tooth wear that occurs over time due to normal chewing and grinding actions. This natural wear happens as the teeth make contact with each other during various activities such as eating, speaking, and grinding. Unlike teeth abrasion, which is caused by external factors like aggressive brushing or abrasive toothpaste, teeth attrition is a result of the normal function of the teeth.
Here are some key points about teeth attrition:
Teeth attrition is a natural process that occurs over time, but its effects can be managed through preventive measures and regular dental care. If you're experiencing tooth sensitivity, changes in bite, or other concerns related to tooth wear, consult your dentist for advice on appropriate treatments and strategies to protect your teeth.